Data Communication
| Created by | Borhan |
|---|---|
| Last edited time | |
| Tag |
Chapters : 01-06, 08, 10, 12
References :
- Data Communication and Networking - Behrouz A. Forouzan
- Mumbai University Archives
- Articles
Chapter 01: Introduction
Data: Data refers to the raw facts that are collected.
Information: Information refers to processed data that enables us to take decision.
Data Communication: Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices by some form of transmission medium such as a wire cable.
The effectiveness of data communication:
- Delivery : Deliver data to the correct destination.
- Accuracy : Deliver the data accurately.
- Timeliness : Deliver data in timely manner. Audio and Video data has to be delivered in a timely manner without any delay; such a data delivery is called real time transmission of data.
- Jitter : It is the variation in the packer arrival time. Uneven jitter may affect the timeliness of data being transmitted.
The components of data communication: There are five components.
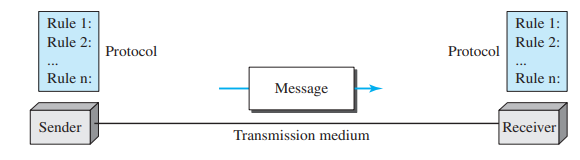
- Message: the information or data to be communicated
- Sender: the device that sends the data message.
- Receiver: the device that receives the message.
- Transmission medium: the physical path by which a message travels from sender to receiver.
- Protocol: A protocol is a set of rules that govern data communication. It is an agreed upon set or rules used by the sender and receiver to communicate data. Without protocol, they may be connected but not communicating.
Data Representation
| Text | Numbers | Images | Audio | Video |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - Represented by bit pattern, a sequence of bit. - Encoding System: ASCII, Unicode | - Stored as a patter of bits | - A pixel is the smallest element of an image represented by bits. - Image is a matrix of pixels | - the recording or broadcasting of sound or music - Continuous signal | - the recording or broadcasting of a picture or movie. |
Data flow
Data flow is the movement of data through a system comprised of software, hardware or a combination of both.
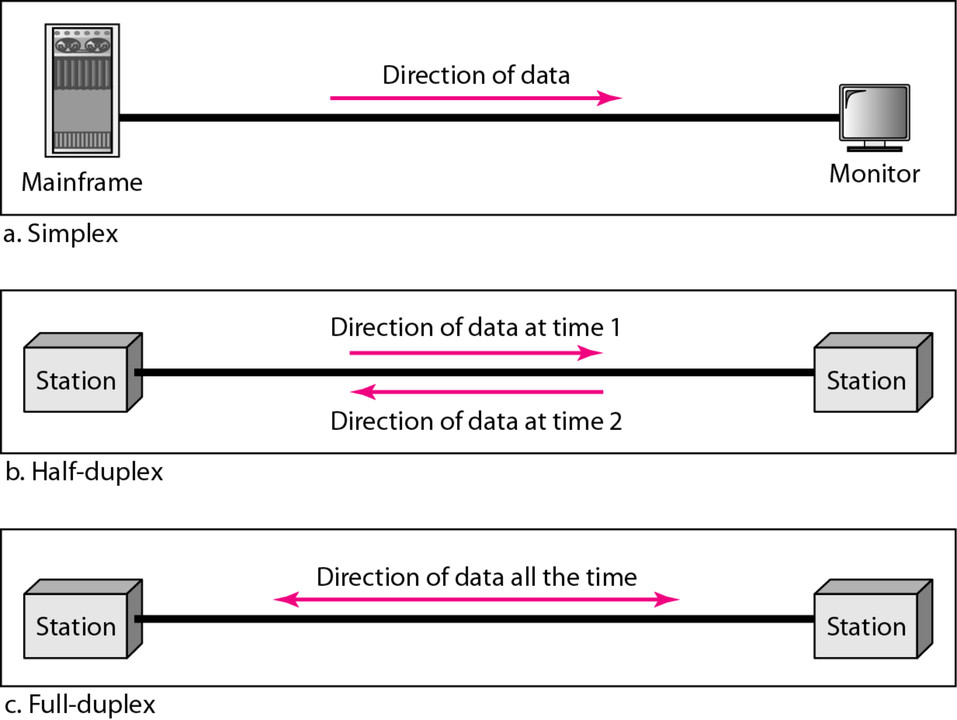
| Basic for Comparison | Simplex | Half Duplex | Full Duplex |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direction of Communication | Unidirectional | Two-directional, one at a time | Two-directional, simultaneously |
| Send/Receive | The sender can only send data | The sender can send and receive data, but one a time | The sender can send and receive data simultaneously |
| Performance | Worst | Better | Best |
| Example | Keyboard | Walkie-Talkie | Telephone |
Network
A network is the interconnection of a set of devices capable of communication.
- Host
- Connecting-device: connects the network to other networks, router
- Switch: connects devices together, modem
A network criteria:
| Reliability | Security | Performance | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Measured by | - the frequency of failure - the time it takes a link to recover from a failure | - protecting data from unauthorized access, damage and development | many ways - transit time, response time - achieving by higher throughput and smaller delay |
Type of Connection
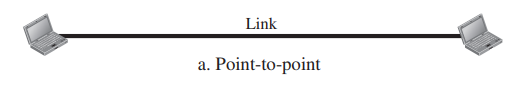
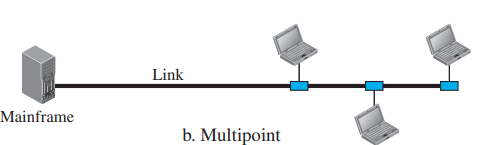
| Basis for Comparison | Point-to-Potin Connection | Multipoint Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | a dedicated link between two devices | more than two devices share a single link |
| Sender/Receiver | there is one transmitter and one receiver | one transmitter but many receivers |
| Security | Provides security | Doesn’t provide security and privacy |
| Complexity | Simple and Straightforward | Complex |
| Cost | Costlier | Lower |
| Suitability | Ideal for dedicated, reliable communications | Beneficial for integrated systems with multiple devices |
Physical Topology
The term physical topology refers to the way in which a network is laid out physically.
| Topology | How does it works? | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
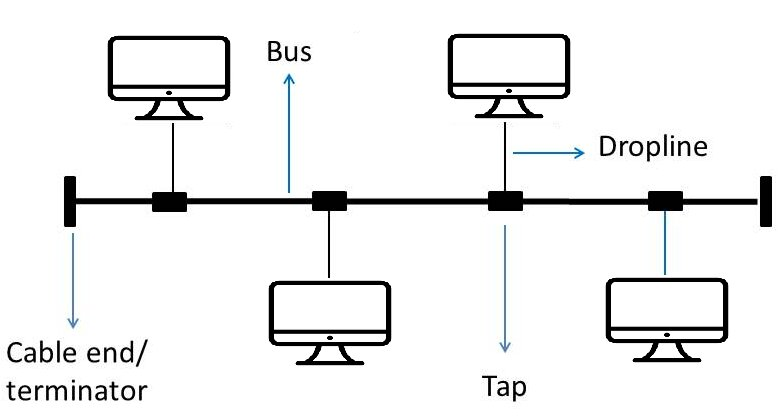
| Bus | - All device connected to a single cable, with terminators at each end. The main cable serves the network’s spine. All nodes are linked to the Taps and Drop lines. Drop lines are the connection between the bus and the nodes. The taps are three way connector that aids in connecting the dropline to the main central cable. - The travels only one direction, and when it reaches the end the terminal removes it. one computer acts as a server and other computers act as clients. Example: Connection two floors with a single line. | - Less Cabling - Less Expensive - Small network - Upgradeable | - Reduced signal strength - Core failure - Low Security |
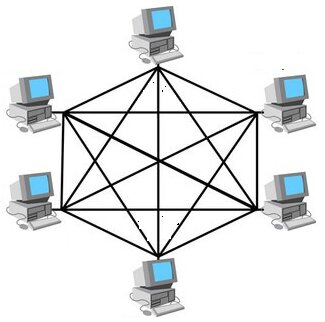
| Mesh | - Every device has a dedicated point to point link to every other device. Duplex-mode links : n*(n-1)/2 n : Total Nodes Fully-connected mesh : each computer is linked with all Partially connected mesh: only specific computers are connected to those with whom they frequently communicate Example: Internet | - Consistent : reliable - High-speed information exchange - Easier reconfiguration | - Costly - High-maintenance - Reducing network efficiency |
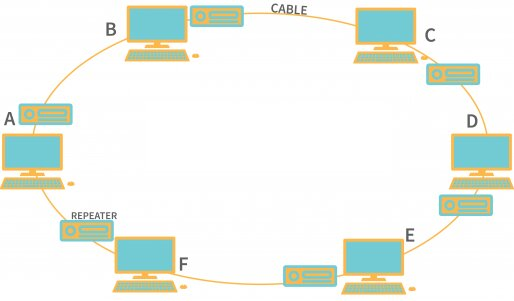
| Ring | - Devices are connected in a closed loop, with each device connected to two other devices. The last computer is linked to the first, forming a loop. Each computer has exactly two neighbors. The central computer in this topology is the monitor station, which in charge all operations. Devices use tokens for data transmission between them. The computer station must have the token to transmit data. The token is released when the transmission ends, and other computer stations can use it to send data. Example: Industrial Control System, where device are interconnected in a ring to monitor and control processes. | - Token System - Less Cabling - Easier troubleshooting | - Difficult to upgrade - When one system crashes, it disturbs the overall network activity. |
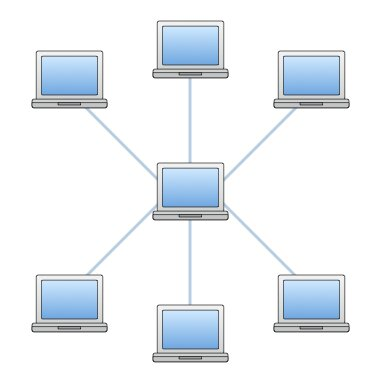
| Star | - All devices are connected to a central hub or switch. Each node is connected to the hub with a point-to-point connection. All traffic passes through the hub that serves a repeater. | - Easy to install and wire. - No disruptions to the network when connecting or removing. - Easy to detect faults and remove parts. | - Requires more cable length - If the hub, switch or concentrator fails, nodes attached are disables. - Expensive |
Consideration When Choosing a Topology: Money. Length of cable needed, Future growth, Cable type
Network Types
| Basis for Comparison | LAN | MAN | WAN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full form | Local Area Network | Metropolitan Area Network | Wide Area Network |
| Definition | LAN is a network that usually connects a small group of computers in a given geographical area | MAN is comparatively wider network that covers large region, like towns and cities. | The WAN network spans to an even large locality - like various countries together. |
| Ownership | Private hospitals, home, schools, office | Can be both private or public. Many organizations and telecom operators. | Can be both private or public. |
| Maintenance and design | Easy | Comparatively difficult | Very difficult |
| Speed | High | Moderate | Low |
| Propagation delay | Very short | Moderate | High |
| Faulty Tolerance | Better | Lesser | Lesser |
| Communication on allotment | Typically allows a single pair of devices to communicate. But it may support more too. | Allows multiple computers to interact simultaneously with each other. | A huge group of computers can easily interact with each other. |
| Congestion | Very low | Higher | Higher |
Chapter 02: Network Models
Protocol Layering: A layer protocol architecture provides a conceptual framework for diving the complex task of exchanging information between remote hosts into simpler task.
Principle of Protocol Layering:
- First Principle : The first principle dictates that if we want bidirectional communication, we need to make each layer so that it is able to perform two opposite task, once in each direction.
- Second Principle: The second principle that we need to follow in protocol layering is that the two objects under each layer at both sides should be identical.
Internet Protocol Suite/ TCP/IP : The internet protocol suite, commonly knowns as TCP/IP, is a framework for organizing the set of communication protocols used in the internet and similar computer net
Layered Architecture
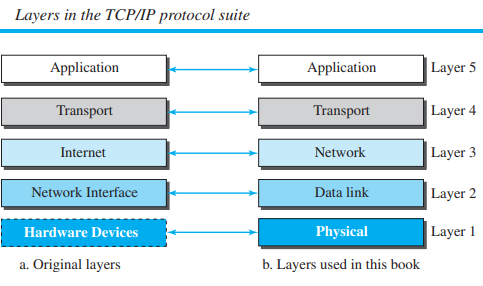
OSI : Open System Interconnection
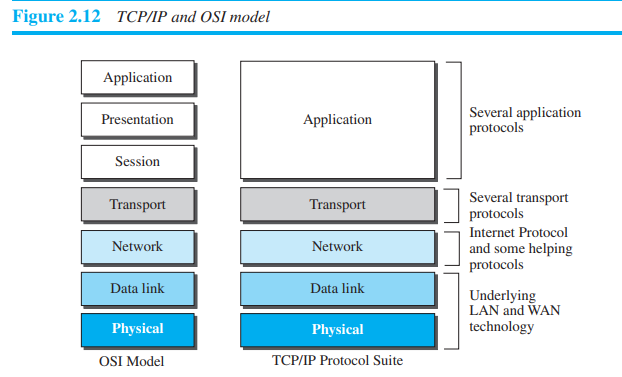
Description of Layers in OSI Model
- Physical Layer
- The physical layer provides a standardized interface to physical transmission media.
- On the sender side → it receives data from Data Link layer and encodes it to signals to be transmitted.
On the receiver side → it receives the signal from the transmission medium decodes it back into data and sends it to Data Link Layer.
- Data Link Layer
- The Data Link layer adds reliability to the physical layer by providing error detection and correction mechanism.
- On the sender side → It receives the data from Network Layer and divides the stream of bits into fixed size manageable units called as Frames and sends it to the physical layer.
On the receiver side → It receives data from Physical Layer and regroups them intro frames and sends them to Network layer. This process is called Framing.
- Physical Addressing : The data link layer appends the physical address in the header of the frame before sending it to physical layer. Physical layer contains sender and receiver.
- Flow control: It makes sure that the sender sends the data at a speed at which receiver can receive it.
- Error control: The data link layer imposes error control mechanism to identify lost or damaged frames, duplicate frames and the retransmit them.
- Main responsibility: hop to hop transmission of frames.
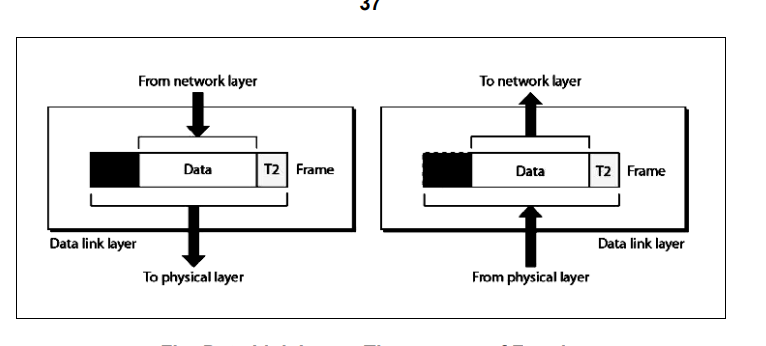
- Network Layer
- The network layer makes sure that the data is delivered to the receiver despite multiple intermediate devices.
- Sending side → it accepts data from transport layer divides in into packets, adds addressing information in the header and passes it to the data link layer.
Receiving side → It receives the frames from data link layer, converts them into packets, verifies the physical addresses and send the packets to the transport layer.
- The network layer is responsible for source to destination of delivery of data.
- Logical addressing: The network layer uses logical address commonly known as IP address to recognize devices on the network.
- An IP address is a universally unique address which enables the network layer to identify devices outside the sender’s network.
- Routing: The network layer divides data into units called packets of equal size and bears a sequence number for rearranging on the receiving end.
- Every packets is independent of the other and may travel using different routes to reach the receiver hence may arrive out of at the receiver.
- The process of finding the best path is called as Routing, using routing algorithms.
- It doesn’t perform any flow control or error control.
- Main responsibility: Transmission of packets from source to destination.
- Transport Layer
- The transport layer takes care of process to process delivery of data and makes sure that it is intact and in order.
- Sending side → the transport layer receives data from the session layer, divides it into unit called segments and sends it to the network layer.
Receiving side → It receives packets from network layer, converts and arranges proper sequence of segments and sends it to the session layer.
- To ensure process to process delivery it makes sure of port address to identify the data from the sending and receiving process.
- A port address is the name or label given to a process. It is a 16 bit address. HTTP use port address 80.
- Error control and flow control
- Session Layer
- The session layer establishes a session between the communicating devices called dialog and synchronizes their interaction.
- Sending side → Accept data from presentation layer adds checkpoint to it called syn bits and passes the data to the transport layer.
Receiving side → It receives data from transport layer removes the checkpoints inserted previously and passes the data to the presentation layer.
- The checkpoint or synchronization points is a way of informing the status of the data transfer.
- Presentation Layer
- The presentation layer performs translation, encryption and compression of data.
- Sending side → It receives data from the application layer adds header which contains information related to encryption and compression and sends it to the session layer.
Receiving side → It receives data from session layer decompresses and decrypts the data as required and translates it back as per the encoding scheme used at the receiver.
- Translation: The sending and receiving device may run on different platforms. Hence, a translation service may be required.
- Compression: It ensures faster data transfer. The data compressed at sender has to be decompressed at the receiving end.
- Encryption: It is the process of transforming the original message to change its meaning before sending it. The revers process called decryption has be performed at the receiving end to recover the original message.
- Application Layer
- Main responsibility: provide access to network resources
- The application layer enables the user to communicate its data to the receiver by providing certain services.
- Once the data is ready, the application layer initiates communication with the corresponding application on another device. This involves establishing a connection, if necessary, and sending the data packets over the network.
- Once the data packets are processed, the application layer delivers the data to the appropriate user application running on the receiving device. This enables the application to interpret and utilize the received data for further processing or display to the user.
- Ensures effective communication with another application program on a network.
- Facilitating communication between clients and server.
- User Authentication and authorization
- Error handling and recovery
Multiplexing and Demultiplexing
- Multiplexing at the source and demultiplexing at the destination
- Multiplexing → A protocol at a layer can encapsulate a packet from several next-higher-layer protocols
- Demultiplexing → A protocol can decapsulate and deliver to a several next-higher layer protocols
Chapter 03: Introduction to Physical Layer
| Analog Data | information that is continuous | Human voice |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Data | information that has discrete states | Data are stored in computer in the form of 0s and 1s |
| Periodic Signal | Signals which repeat itself after a fixed time period |
|---|---|
| Non-periodic Signal | Signal which do not repeat itself after a fixed time period |
Analog Signal
- They have infinite value in a range
Characteristics of an analog signal (Sine wave is analog) : 3 characteristics
Peak Amplitude
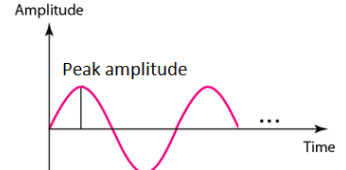
- The peak amplitude of a signal is the absolute value of the highest intensity
- The amplitude of a signal is proportional to the energy carried by the signal
Frequency and Period
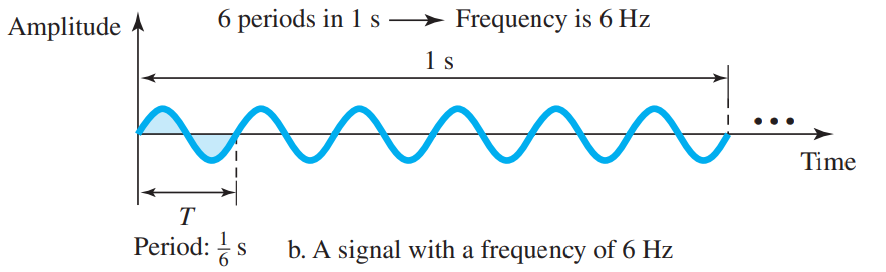
- Frequency refers to the number of cycles completed by the wave in one second.
Frequency is the rate of change w.r.t time.
If signal doesn’t change at all, is . If it changes instantaneously, is
Frequency is independent of the medium
- Period refers to the time taken by the wave to complete one cycle
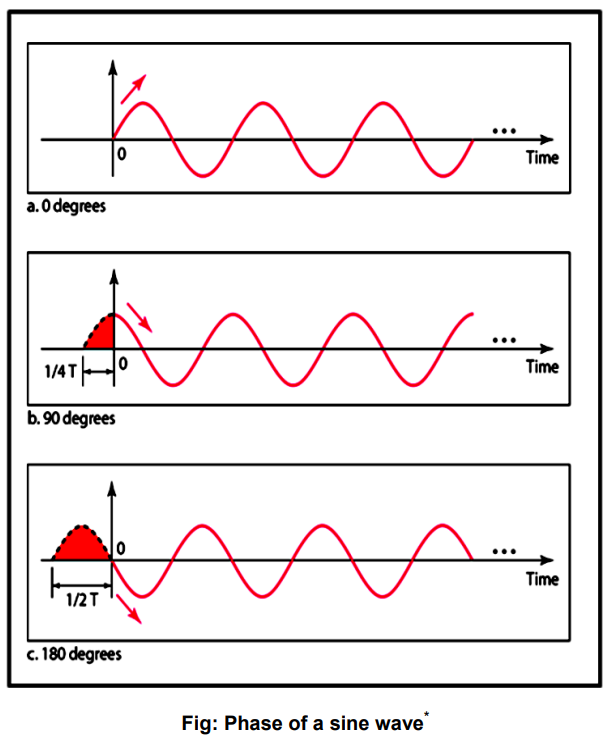
Phase
- Phase describes the position of the waveform w.r.t time.
- Phase indicates the forward and backward shift of the waveform from the axis.
- It is measured in degrees or radian
Example: A sine wave is offset cycle w.r.t time. What is phase degrees in degrees and radian.
Wavelength
- The wavelength is the distance a signal travels in one period.
- It is depends on medium and frequency
- It is measured in micrometers
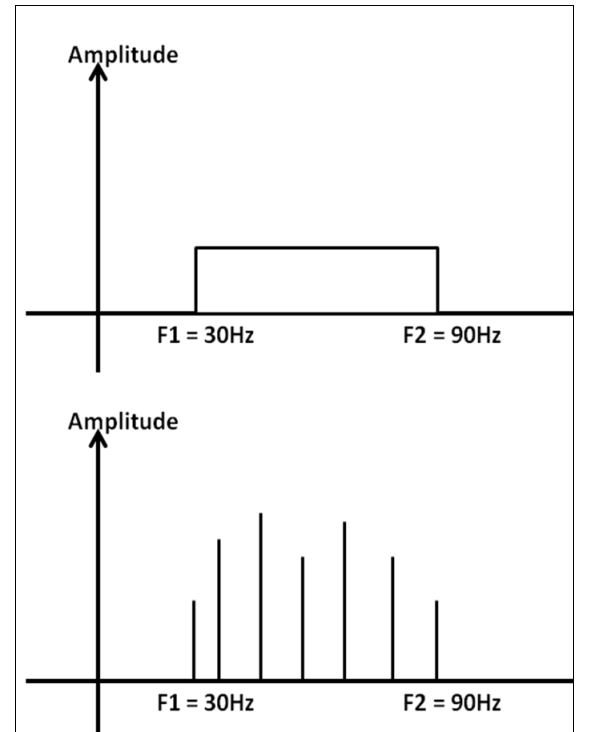
Time Domain and Frequency Domain
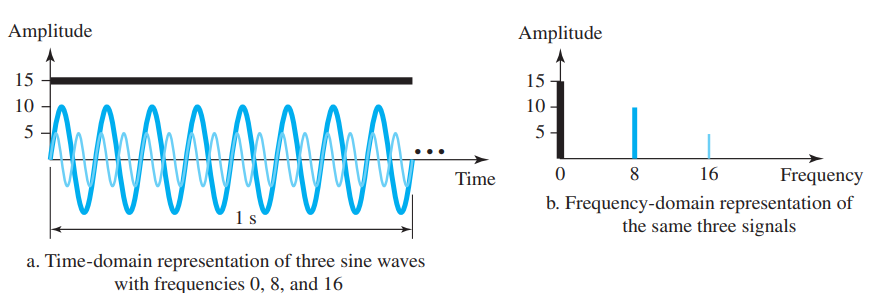
- The time-domain plot shows the changes in signal amplitude w.r.t time. Time-amplitude relation.
- The frequency-domain plot shows the signal frequency and peak amplitude.
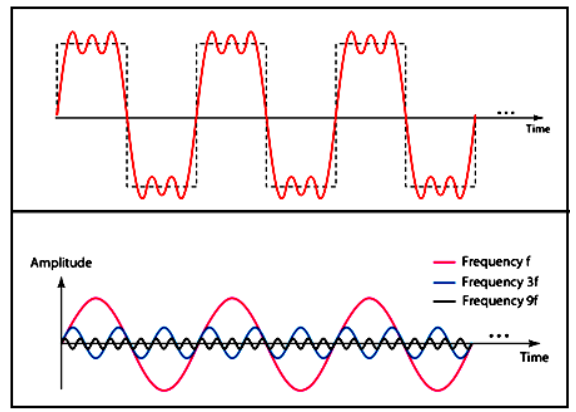
Composite Signal
- A composite signal is a combination of two or more simple sine waves with different frequency, phase and amplitude
- A periodic composite signal can be decomposed into a series of signals with discrete frequencies.
- A non-periodic signal when decomposed gives a combination of sine waves with continuous frequencies.
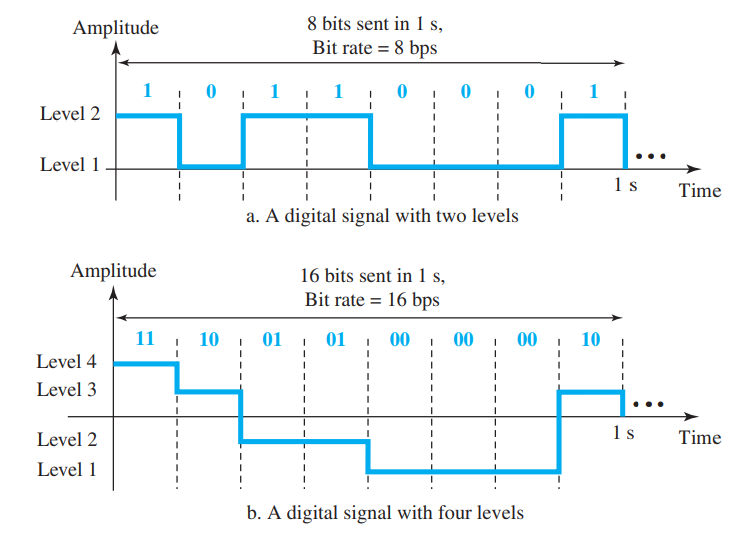
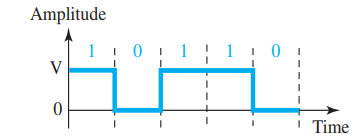
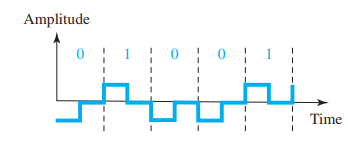
Digital Signal
- They have limited number of defined values
- Information in digital signal can be explained in the form of voltage levels
- If a signal has levels, each level need bits.
Bit Length or Interval
- The bit length is the distance one bit occupies on the transmission medium
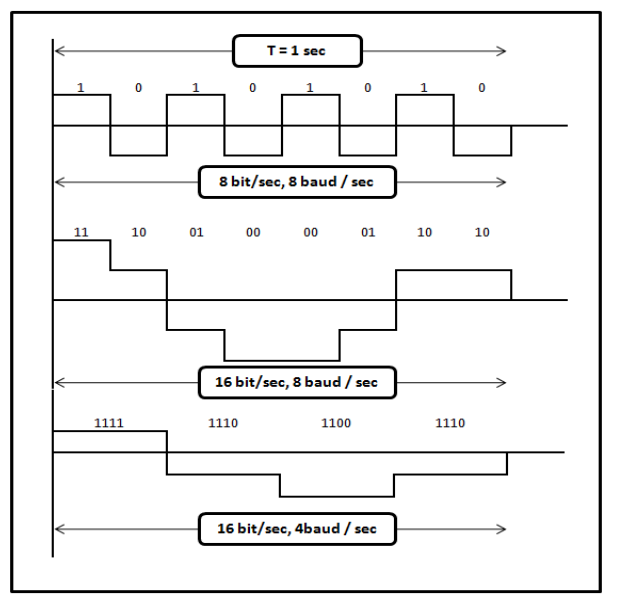
Bit Rate
- It is the the number of bits transmitted in one second
- Expressed as bits per second (bps)
Example: An analog signal carries 4 bits in each signal unit. If 1000 signal units are send per second. Find the baud rate and bit rate.
Baud rate : 1000 bauds
Bit rate = 4 * 1000 = 400 bps
Channel
- A channel is the medium through which the signal carrying information will be passed
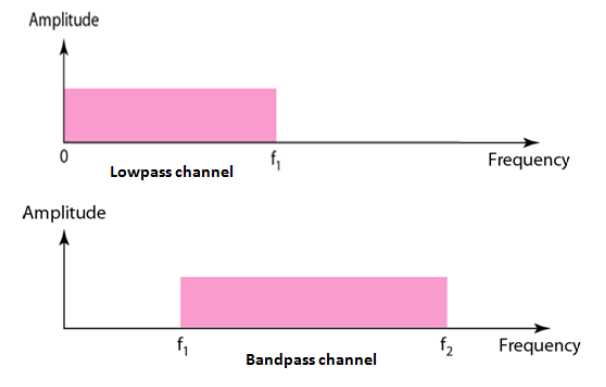
Types of Channels
| Low Pas Channel | Band Pass Channel |
|---|---|
| The channel has the lowest frequency as 0 and highest frequency as some non zero frequency f1. | The channel has the lowest frequency as some non-zero frequency ‘f1’ and highest frequency as some non-zero frequency ‘f2’ |
| This channel can pass all the frequencies in the range 0 to f1. | The channel can pass all frequencies in the range f1 to f2. |
| Rough Approximation (minimum) : N/2 First two harmonics : 3N/2 First three harmonic : 5N/2 N = frequency |
- Transmission of Digital Signal
| Baseband Transmission | Broad band transmission |
|---|---|
| The signal is transmitted without making any change to it | A digital signal cannot be transmitted directly through it |
| The bandwidth of the signal to be transmitted has to be less than the bandwidth of the channel | We use modulation. We change the signal to analog signal before transmitting it. |
| Ex. Consider a Baseband channel with lower frequency 0Hz and higher frequency 100Hz, hence its bandwidth is 100. We can easily transmit a signal with frequency below 100Hz. Logically a signal with frequency say 120Hz will be blocked | Ex. Consider the bandpass channel with lower frequency 50Hz and higher frequency 80Hz, and the signal to be transmitted has frequency 10Hz. To pass the analog signal through the bandpass channel, the signal is modulated using a carrier frequency. The analog signal (10Hz) is modulated by a carrier frequency of 50Hz resulting in an signal of frequency 60Hz which can pass through our bandpass channel. |
Bandwidth
- Bandwidth can be defined as the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum occupied by the signal.
- It may be defined as the frequency range over which a signal transmitted.
Bandwidth of an analog signal:
- Bandwidth of an analog signal is expressed in term of its frequencies.
- It is calculated by the difference between the maximum and minimum frequency.
Bandwidth of an digital signal
- It is defined as the maximum bit rate of the signal to be transmitted
- it is measured in bits per second
Bandwidth of a Channel
- In terms of analog signal, bandwidth of the channel is the range of frequencies that the channel can carry.
- In terms of digital signal, bandwidth of the channel is the maximum bit rate supported by the channel.
- The Channel bandwidth determines the type of signal to be transmitted.
Attenuation : It means a loss of energy. When a signal travels through a medium, it loses some of its energy in overcoming the resistance.
Distortion: It means that the signal changes its form or shape. It can occur in a composite signal made of different frequencies. Each signal has its own propagation speed through a medium and therefore its own delay in arriving at the final destination.
SNR : Signal to Noise Ratio
The maximum data rate of a channel
Data rate depends on three factors:
- The bandwidth available
- The level of the signal we use
- The quality of the channel (noise level)
The Quality of the channel
| Noiseless or Perfect Channel | Noisy Channel |
|---|---|
| An ideal channel with no noise | A realistic channel that has some noise |
| The Nyquist bit rate gives the bit rate | The Shannon Capacity gives the bit rate |
Nyquist Bit Rate
Shannon Capacity
- SNR is the Signal to Noise Ratio
- Measured in bps
Propagation time : Time required for a bit to travel from the source to the destination.
Transmission Time
Chapter 05: Digital Transmission
Line Coding
- It is the process of converting digital data to digital signals.
-
-
-
Example: A signal is carrying data in which one data element is encoded as one signal element (r = 1). If the bit rate is 100 kbps, what is the average value of the baud rate if c is between 0 and 1?
Line coding scheme line
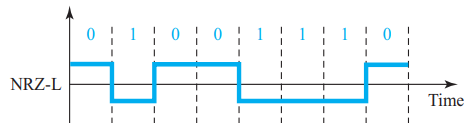
- Unipolar
all the signal levels are on one side of the time axis
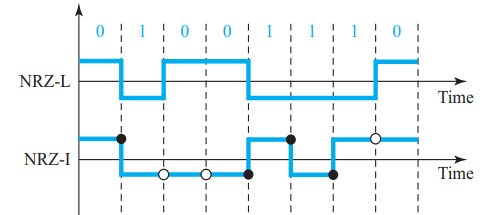
- Polar
In polar schemes, the voltages are on both sides of the time axis.
NRZ-L and NRZ-I both have an average signal rate of N/2 Bd.
Polar RZ (Return to Zero)
Polar Manchester
Polar Differential Manchester
- Bipolar
Bipolar RZ
Bipolar AMI
Bipolar Pseudoternary
Skipped.
Chapter 05 : Analog Transmission
Digital to Analog Conversation
It is the process of changing one of the characteristics of an analog signal based on the information in digital data.
;
Analog Transmission
A method of sending/transmitting information over long distance by encoding it as an analogue signal.
Carrier Signal
In analog transmission. the sending device produces a high-frequency signal that acts as a base for the information signal. The base signal is known as carrier signal or frequency.
Chapter 06
Frame Size = Number of source * output slot carries + synchronization bit
Frame rate = source bandwidth/output slot carries
Frame duration = 1/frame rate
Data rate = frame rate * frame size
Efficiency =
PCM bandwidth :
- Assume that a voice channel occupies a bandwidth of 4 kHz. We need to multiplex 10 voice channels with guard bands of 500 Hz using FDM. Calculate the required bandwidth. Find the maximum effect of a 2-ms burst of noise on data transmitted a 12000 bps.
10*4*1000 + 9*500
2*10^-3 *12000
- What is the minimum number of bits in a pseudorandom noise (PN) sequence if we use FHSS with a channel bandwidth of B = 4 KHz and Bss = 128 KHz?
The number of hops = 100 KHz/4 KHz = 25. So we need log225 = 4.64 ≈ 5 bits
| Sr. No | Hub | Switch | Router |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hub is a physical layer device i.e. layer 1. | Switch is a data link layer device i.e. layer 2. | Router is a network layer device i.e. layer 3. |
| 2. | A Hub works on the basis of broadcasting. | Switch works on the basis of MAC address. | A router works on the basis of IP address. |
| 3. | A Hub is a multiport repeater in which a signal introduced at the input of any port appears at the output of the all available ports. | A Switch is a tele-communication device which receives a message from any device connected to it and then transmits the message only to the device for which the message is intended. | A router reads the header of incoming packet and forward it to the port for which it is intended there by determines the route. It can also perform filtering and encapsulation. |
| 4. | Hub is not an intelligent device that may include amplifier on repeater. | A Switch is an intelligent device as it passes on the message to the selective device by inspecting the address. | A route is more sophisticated and intelligent device as it can read IP address and direct the packets to another network with specified IP address. Moreover routers can built address tables that helps in routing decisions. |
| 5. | At least single network is required to connect. | At least single network is required to connect. | Router needs at least two networks to connect. |
| 6. | Hub is cheaper as compared to switch and router. | Switch is an expensive device than hub. | Router is a relatively much more expensive device than hub and switch. |
| 7. | Speed of original hub 10Mbps and modern internet hub is 100Mbps. | maximum speed is 10Mbps to 100Mbps. | maximum speed for wireless is 1-10 Mbps and maximum speed for wired connections is 100 Mbps. |
| 8. | Hubs are used in LANs. | Switch is used in LANs. | Routers are used in LANs, MANs and WANs. |